How Lono Works
Here is a diagram and high-level explanation that describes how lono works.
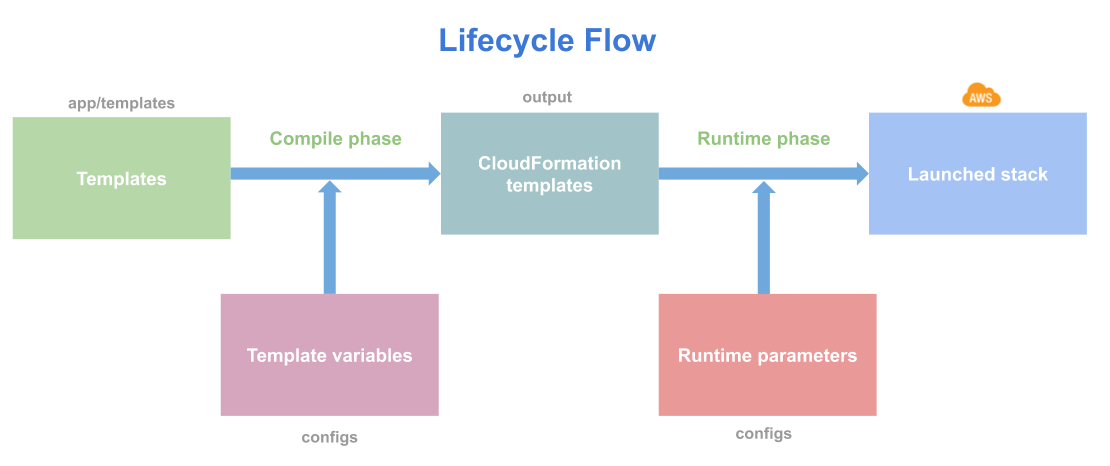
Lono works by building a CloudFormation template from a Lono blueprint. The blueprint is written in a DSL. The DSL looks this:
app/blueprints/demo/template.rb
parameter("BucketName", Conditional: true)
parameter("AccessControl", Default: "Private")
resource("Bucket", "AWS::S3::Bucket",
BucketName: ref("BucketName", Conditional: true),
AccessControl: ref("AccessControl"),
)
output("BucketName", ref("Bucket"))
The built CloudFormation YAML looks like this:
output/demo/template.yml
---
Parameters:
BucketName:
Default: ''
Type: String
AccessControl:
Default: Private
Type: String
Conditions:
HasBucketName:
Fn::Not:
- Fn::Equals:
- Ref: BucketName
- ''
Resources:
Bucket:
Type: AWS::S3::Bucket
Properties:
BucketName:
Fn::If:
- HasBucketName
- Ref: BucketName
- Ref: AWS::NoValue
AccessControl:
Ref: AccessControl
Outputs:
BucketName:
Value:
Ref: Bucket
Lono then simply calls the CloudFormation API with the CloudFormation template and parameters. In fact you can even use the built files and call the CloudFormation API directly with the CLI.
lono build demo
cd output/demo
aws cloudformation create-stack --stack-name demo-dev --template-body file://template.yml --parameters file://params.json
Lono automates the full process with:
lono up demo
